In the field of metal fabrication, choosing the right cutting method is critical to achieving efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Two widely used methods are laser cutting and flame cutting (also known as oxy-fuel cutting). While both techniques are used to cut metal, they differ significantly in terms of technology, capabilities, materials, and application. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers select the best method based on project requirements.
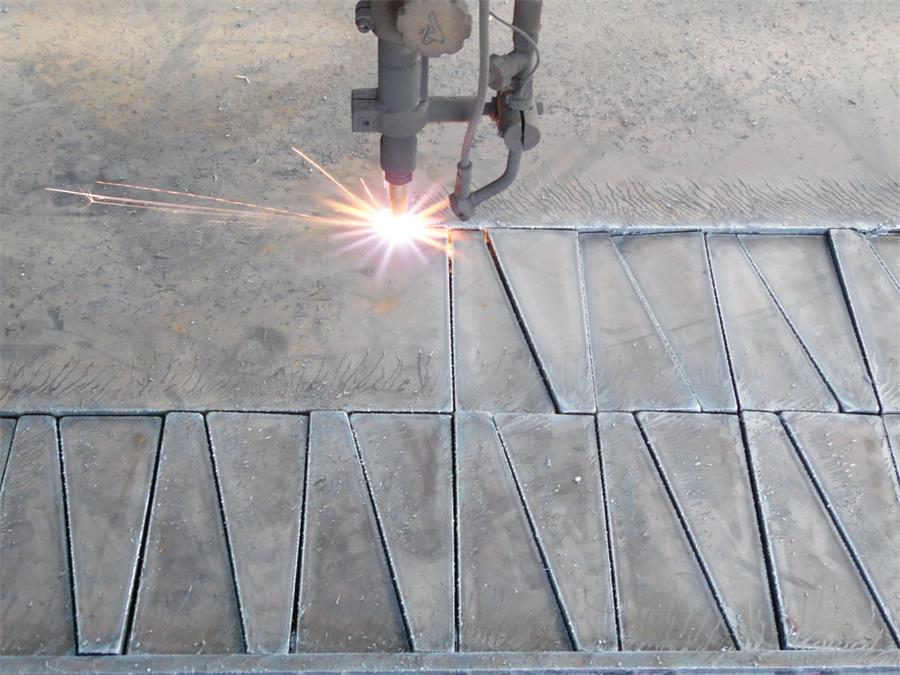

1. Cutting Method and Technology
Laser cutting uses a high-powered, focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material along a cutting path. The laser is guided by computer numerical control (CNC) to achieve precise and complex shapes. The laser can be CO₂-based or fiber-optic, depending on the machine and material.
Flame cutting, on the other hand, uses a mixture of oxygen and a fuel gas (like acetylene, propane, or natural gas) to produce a high-temperature flame. This flame heats the metal to its ignition temperature, after which a jet of pure oxygen is directed onto the material to oxidize and blow away the molten metal, completing the cut.
2. Material Suitability
Laser cutting works best on thinner materials, typically up to 25 mm for carbon steel, and can also cut stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It’s ideal for materials that require high precision and minimal heat distortion.
Flame cutting is primarily used for thicker carbon steel plates, often up to 300 mm or more. However, it is not suitable for cutting stainless steel or non-ferrous metals, as they do not oxidize in the same way carbon steel does.
3. Cut Quality and Precision
Laser cutting offers superior edge quality, cleaner cuts, and high dimensional accuracy. It’s capable of creating intricate designs, tight tolerances, and smooth finishes with minimal post-processing.
Flame cutting, while effective on thick steel, produces a rougher edge and wider kerf (cut width). It may require additional grinding or finishing, especially when high precision is needed.
4. Speed and Efficiency
Laser cutting is generally faster on thin to medium-thickness materials, especially when complex shapes or small features are involved. It's also more energy-efficient for lighter jobs.
Flame cutting is slower, particularly on thinner materials, but it remains a cost-effective option for cutting thick carbon steel, where other cutting methods may struggle or require more expensive equipment.
5. Cost and Equipment Investment
Laser cutting systems are more expensive to purchase and maintain due to their advanced technology and sensitive components. They also require skilled operators and a controlled environment to ensure consistent quality.

Flame cutting equipment is relatively affordable and easy to operate, making it a practical choice for many heavy-duty industrial applications. However, the ongoing cost of fuel and the need for post-processing can add to the total cost over time.
In summary, laser cutting is best suited for applications that demand high precision, clean edges, and fast turnaround on thinner materials. Flame cutting is ideal for heavy-duty cutting of thick carbon steel, where precision is less critical, but strength and depth are key. The choice between the two depends on the material type, thickness, desired cut quality, production speed, and budget.
Both techniques have their strengths, and in many workshops, they are used side by side to handle different types of cutting jobs efficiently.